
A bone scan is a crucial diagnostic tool in the fight against cancer, offering detailed insights into the health and condition of the bones. This imaging technique is vital for detecting the presence of cancerous cells in the bones, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment, and evaluating other conditions affecting bone health. Understanding how bone scans work and why they are used can empower patients and caregivers with valuable knowledge during their healthcare journey.
At its core, a bone scan involves the use of a small amount of radioactive material, known as a tracer. This tracer is injected into the bloodstream and travels to areas of the bone that are in the process of repairing themselves or are undergoing increased metabolic activity a common indicator of bone cancer or metastasis. After the tracer has been given adequate time to circulate, a special camera takes images of the skeleton, highlighting areas of potential concern.
Bone scans are an essential component of the diagnostic process for various cancers due to their sensitivity to changes in bone metabolism. They are particularly useful for identifying metastatic bone disease, where cancer from another part of the body has spread to the bones and primary bone cancers. Bone scans also play a critical role in assessing the efficacy of ongoing treatments, allowing healthcare providers to adjust therapeutic approaches based on real-time feedback about the cancer response.
Several types of cancer are commonly linked with bone involvement, making bone scans a vital diagnostic tool. These include:
Preparation for a bone scan is generally minimal, with patients usually instructed to stay hydrated and possibly fast for a few hours before the test. Patients need to inform their healthcare provider about any medications or supplements they are taking, as certain substances can interfere with the results of the scan.
Bone scans are a pivotal part of diagnosing and managing cancer, offering a detailed picture of bone health that other tests might miss. By highlighting active problem areas within the bones, these scans play a critical role in the early detection of cancer metastasis and the monitoring of treatment efficacy. Understanding the function, purpose, and process of bone scans can demystify this important diagnostic tool, making the cancer treatment journey a little less daunting for patients and their loved ones.
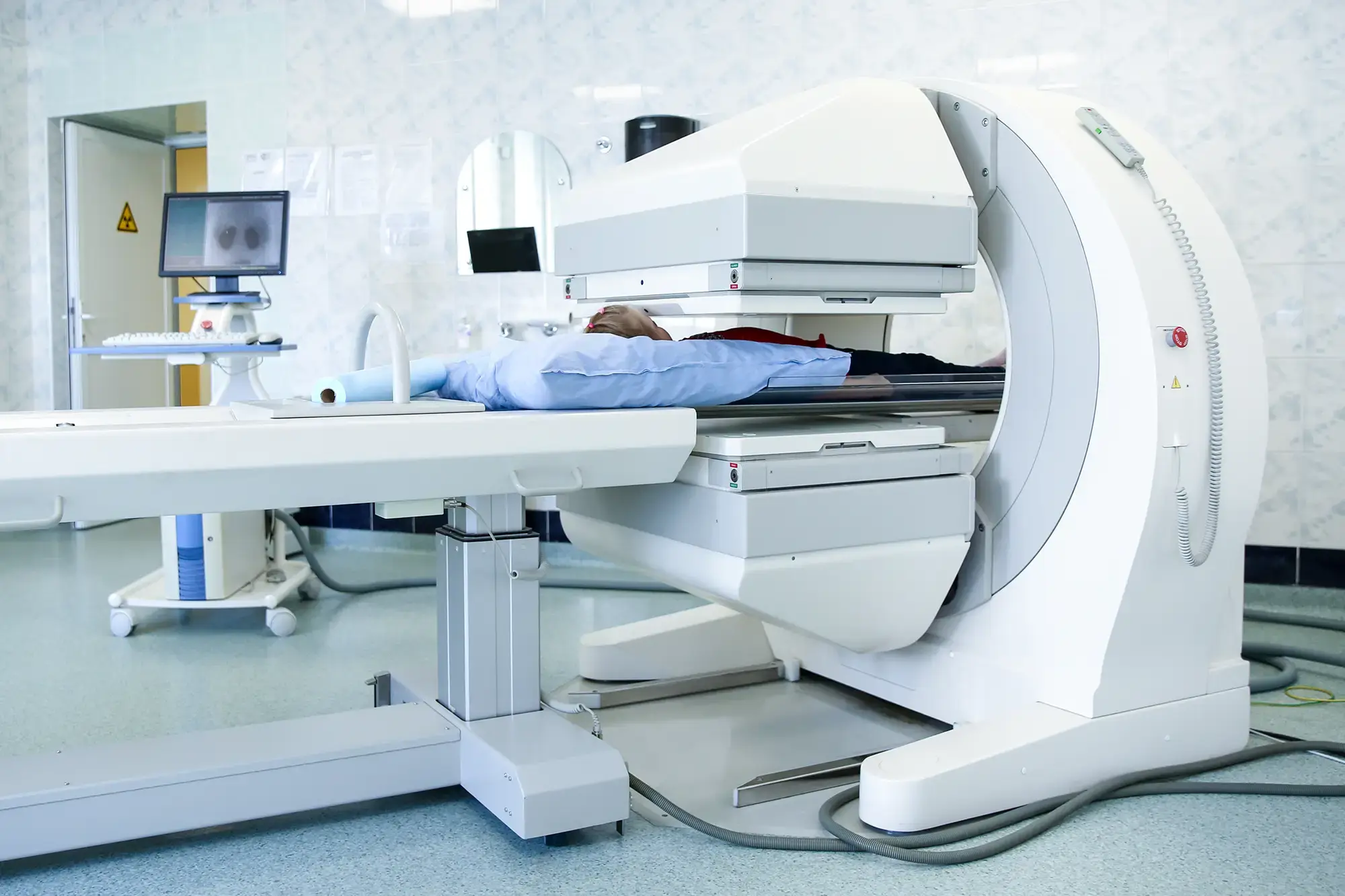
If you or a loved one is preparing for a bone scan to check for cancer, it's normal to feel a bit anxious about the process. However, understanding what to expect and how to prepare can make the experience smoother and less stressful. Below, find practical advice to help you get ready for your bone scan appointment.
Dietary Restrictions
Generally, there are no strict dietary restrictions before a bone scan. However, staying hydrated is crucial. Drinking plenty of water the day before and the day of your scan can help improve the quality of the images produced. Avoid caffeinated beverages as they can lead to dehydration. As for food, sticking to easy-to-digest, healthy vegetarian meals is wise. Foods rich in calcium such as spinach, kale, and almonds can be beneficial. Remember to avoid any dietary supplements or medications that may contain barium or bismuth for at least four days before the scan, as they can interfere with the results.
What to Expect During the Procedure
Upon arrival, you'll likely be given a small amount of a radioactive tracer through an injection. This tracer travels through your bloodstream and into your bones. It's crucial to note that the amount of radiation is very low and considered safe. After the injection, there might be a waiting period before the scan begins to allow the tracer to properly distribute throughout your body.
The bone scan itself is painless. You'll lie on a table while a camera scans your body. It's important to remain as still as possible during this time to ensure clear images. If you're claustrophobic or uncomfortable in tight spaces, let your technician know. They can provide you with strategies to help you feel more comfortable.
Duration of the Scan
The entire process for a bone scan can vary in length, but generally, the scanning portion takes about 30 to 60 minutes. Including the waiting time after the tracer injection, you may be at the facility for several hours. Planning your day accordingly and bringing something to read or an activity to pass the time can be helpful.
After the Scan
Post-scan, drinking plenty of water will help flush the tracer out of your system faster. You can resume your regular diet immediately but sticking to healthy, nutritious choices will support your overall well-being. Any side effects are rare, but should you experience anything unusual, contacting your healthcare provider is essential.
Preparing for a bone scan for cancer involves simple but important steps. By following the above tips and having a clear understanding of the process, you can go into your appointment feeling more prepared and less anxious. Remember, your healthcare team is there to support you throughout this process, so don't hesitate to reach out with any questions or concerns you may have.
A bone scan is a pivotal diagnostic tool used in the detection and monitoring of various conditions, including cancer. It relies on the use of a small amount of radioactive material to highlight abnormalities in the bones. Understanding the interpretation of bone scan results is crucial for patients undergoing this procedure as part of their cancer diagnosis or treatment plan. This section will delve into how these results are interpreted, focusing on the distinction between 'hot spots' and 'cold spots' and what they potentially indicate about a patient's health status.
Hot spots are areas on the bone scan that appear brighter or show increased activity. They occur when there is a higher-than-normal accumulation of the radioactive tracer. This could indicate several conditions, including areas of cancer that have spread to the bones (bone metastases), bone infections (osteomyelitis), or other bone diseases. However, it's important to note that hot spots are not solely indicative of cancer; they can also be seen in non-cancerous conditions such as fractures, arthritis, and certain benign bone tumors.
In contrast, cold spots are areas that appear darker on the scan. These spots signify regions where the radioactive tracer is absorbed less than the surrounding tissue. Cold spots can indicate certain types of cancer or be a sign of poor blood supply to the bone (avascular necrosis), among other conditions. However, similar to hot spots, the presence of cold spots does not definitively diagnose cancer and requires further investigation for accurate interpretation.
The interpretation of bone scan results is complex and depends on various factors, including the patient's medical history, the type of cancer suspected, and the presence of symptoms. Radiologists or nuclear medicine specialists typically read and interpret the scans in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and findings to provide a comprehensive assessment of a patient's condition. In some cases, additional imaging tests or biopsies may be recommended to confirm the nature of hot or cold spots detected on the bone scan.
Patients need to discuss their bone scan results thoroughly with their healthcare provider to understand what the findings mean for their specific situation. Remember, while bone scans are a powerful tool in the detection and management of cancer and other bone-related diseases, they are just one part of a larger diagnostic puzzle.
Interpreting bone scan results is a critical step in diagnosing and managing various conditions, including cancer. By differentiating between hot spots and cold spots, healthcare professionals can pinpoint areas of concern and determine the best course of action. Patients are encouraged to engage in open dialogue with their medical team to gain a clear understanding of their bone scan results and the implications for their health.
When it comes to diagnosing cancer, particularly understanding if it has spread to the bones (bone metastases), doctors have several imaging techniques at their disposal. Each of these methods, including bone scans, CT (Computed Tomography) scans, MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scans, offers unique advantages and limitations in detecting bone metastases and other abnormalities.
Bone scans involve the injection of a small amount of radioactive material, which tends to accumulate in areas of the bone that may be damaged or affected by cancer, making these areas visible on the scan. This makes bone scans particularly effective at detecting bone metastases early on, even before they might cause pain or show up on other types of imaging tests.
CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body and are very useful in detecting bone abnormalities caused by cancer. They offer more detailed images than traditional X-rays and can help determine the size and shape of a tumor. However, CT scans may not be as sensitive in detecting early bone metastases as bone scans.
MRI scans give a very detailed image of the body's soft tissues, making them ideal for detecting cancer in organs and tissues but also useful for examining bones. MRIs can show if the cancer has spread to the bone marrow, which often occurs before changes to the bone structure are detectable with other imaging methods. However, getting an MRI is generally more time-consuming and expensive than a bone scan or CT scan.
PET scans, often combined with CT scans (PET-CT), are highly effective at detecting cancer throughout the body, including bone metastases. PET scans can show the metabolic activity of lesions, which can help distinguish between active cancer cells and non-cancerous abnormalities. Despite their sensitivity, PET scans may not always be available or may be expensive.
The choice between a bone scan, CT scan, MRI, or PET scan depends on numerous factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, the patient's overall health, and specific symptoms. In many cases, doctors may recommend a combination of these imaging tests to get a comprehensive understanding of the cancer's spread and impact, particularly on the bones.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each imaging technique is crucial for patients and their caregivers as they navigate cancer diagnosis and treatment. Collaboration with a healthcare team ensures that the right modalities are used at the right time, improving the chances of an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.

Cancer treatment is a journey paved with numerous diagnostic tests and evaluations, among which bone scans hold substantial importance, especially for cancers prone to spreading to the bones. This non-invasive procedure offers critical insights into the effectiveness of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy, playing a pivotal role in tailoring patient care.
When it comes to managing cancer, understanding the progress of the disease and the impact of treatments is vital. Bone scans provide a comprehensive image of bone metabolism, helping doctors to detect any abnormal activity or changes in the bone. This is particularly useful for cancers that have a high risk of bone metastasis, such as breast, prostate, and lung cancers.
How does a bone scan work? A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the bloodstream, which is absorbed by bones with higher than normal activity, indicating areas of concern. These areas, often referred to as hot spots, can signify either the presence of cancer cells or the healing response of bone to treatment such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
One of the primary uses of bone scans in the context of cancer treatment is to monitor the effectiveness of ongoing therapies. By comparing bone scans taken over time, doctors can ascertain if the treatment is successfully targeting and reducing cancer's presence in the bones. Should hot spots begin to diminish in size or number, this typically reflects a positive response to treatment.
Furthermore, bone scans are instrumental in helping healthcare professionals decide whether to continue with a current treatment strategy or to consider alternative methods. This adaptability is crucial for patient outcomes, as it allows for a more personalized approach to cancer care.
While bone scans are invaluable in tracking treatment progress, it's important to remember they are part of a larger diagnostic toolkit. False positives can occur, where non-cancerous conditions such as fractures or infections may appear as hot spots. Hence, bone scan results are usually considered alongside other tests and the patient's overall clinical picture.
In conclusion, bone scans serve as a vital tool in the arsenal against cancer, particularly for monitoring how well treatments are working against cancer that poses a risk to bone health. Through these scans, healthcare providers can offer more targeted and effective care, significantly impacting the journey to recovery.
Understanding the role of bone scans in cancer treatment underscores the advancements in medical technology and their application in providing precise, personalized patient care. As the fight against cancer continues, innovations like bone scans play a critical role in enhancing treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
In recent years, the medical field has seen significant advancements in bone scan technology, especially in the areas of cancer detection and monitoring. These improvements have provided oncologists and radiologists with more precise tools, helping in the early identification and treatment of various cancers.
One of the notable advancements is the introduction of new tracers and imaging agents. Traditionally, Technetium-99m has been widely used in bone scans to detect abnormalities. However, newer tracers like Fluoride-18 (18F), used in PET/CT scans, have shown superior capabilities in identifying even small metastatic lesions, vastly improving the accuracy of diagnosis.
Alongside this, the development of Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) scanning technology has enabled the detailed analysis of bone density, aiding in the early detection of cancers that affect bone density. This technique is particularly beneficial in monitoring the impact of cancer treatments on bone health.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into bone scan technology represents another leap forward. These innovations help in the analysis of scan images, reducing human error, and increasing the speed of diagnosis. AI algorithms can identify patterns and abnormalities that may not be immediately visible to the human eye, thus improving the diagnostic process.
Moreover, advancements in 3D imaging techniques have further enhanced the clarity and depth of bone scans. This technology provides high-resolution images that allow for a more detailed examination of bone structures and abnormalities, leading to more accurate assessments and treatment plans.
In conclusion, the improvements in bone scan technology signify a promising direction in the fight against cancer. With the ongoing research and introduction of innovative tracers, techniques, and AI-driven analysis, the future of cancer detection and monitoring looks brighter. These technological advancements not only boost the accuracy of diagnoses but also play a crucial role in developing more effective treatment strategies for cancer patients, ultimately aiming for better outcomes and quality of life.
For more information on bone health and cancer, stay tuned to our latest posts and updates.

When it comes to battling cancer, every individual's journey is unique. Diagnosing and treating cancer often involves a complex mix of tests and procedures, one of which may be a bone scan. This essential tool helps doctors detect the presence of cancer in bones and assess the effectiveness of ongoing treatment. Let's delve into personal narratives that highlight the significant role of bone scans in cancer management.
Maria's Early Detection Story
Maria, a 55-year-old teacher, never thought a routine health check-up would change her life. She had been experiencing mild back pain but attributed it to her busy schedule. It was her doctor's proactive decision to include a bone scan in her examination that led to the early detection of bone metastasis from breast cancer. Maria reflects, "That bone scan was a turning point for me. It not only helped catch the cancer early but also significantly influenced my treatment plan." Maria underwent targeted therapy, and her latest scans show a positive response to the treatment.
John's Story of Hope
John, who was diagnosed with prostate cancer, faced an uphill battle when his cancer spread to his bones. The pain was unbearable, severely impacting his quality of life. However, a bone scan played a crucial role in identifying the affected areas. "The detailed images from the bone scan provided my oncologist with the information needed to tailor a treatment specifically for my condition," says John. Following his bone scan results, John began a specialized treatment regime that significantly reduced his pain and improved his mobility.
Both Maria's and John's stories underline the critical importance of bone scans in the cancer care continuum. Not only do these scans offer a non-invasive way to monitor disease progression, but they also empower healthcare providers to personalize treatment plans, thereby enhancing the chances of a successful outcome.
While the journey through cancer diagnosis and treatment can be daunting, advancements in medical imaging and personalized care approaches offer hope and support. These personal stories are a testament to the strength found in facing the unknown and the crucial role of technology in navigating the path to wellness.
To those currently undergoing similar challenges, remember, your story is important. Every test, including bone scans, is a step towards understanding your condition better and tailoring your treatment to your specific needs. Stay informed, stay hopeful, and trust in the journey.
As we close, it's worth mentioning the importance of a balanced diet in supporting cancer treatment and recovery. Incorporating whole, plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients and energy needed during this time. Remember, nurturing your body is as crucial as nurturing your spirit on this journey.
Maintaining bone health is crucial for cancer patients, both during and after treatment. The journey through cancer diagnosis, treatment, and recovery can significantly impact bone density and strength, making it essential to focus on strategies to support bone health. Below, we provide insights into dietary recommendations, supplements, and physical activities that can help.
A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining bone health. Foods rich in calcium and vitamin D are particularly important because they are the cornerstones of bone health. Cancer patients are encouraged to include a variety of calcium-rich foods in their diet, such as:
Vitamin D helps your body use calcium, which is why getting enough of it is equally important for bone health. While sunlight is a good source, cancer patients, particularly those undergoing chemotherapy or radiotherapy, may need to limit sun exposure. Vitamin D can also be found in fortified foods and supplements.
Talking to your doctor about supplements is a good step toward maintaining bone health. They might recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements, especially if your dietary intake is insufficient or if you have an increased need for these nutrients. However, it's important to follow their guidance regarding dosage to avoid any adverse effects.
Regular physical activity is beneficial for everyone, including cancer patients. It can help maintain bone density, reduce the risk of osteoporosis, and improve overall well-being. Depending on the individual's health status and the stage of cancer treatment, the following activities might be recommended:
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure it's safe and appropriate for your current health condition.
In conclusion, maintaining bone health in cancer patients requires a multifaceted approach that includes a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, appropriate supplements as recommended by a healthcare provider, and regular physical activity tailored to individual capabilities and treatment stages. By prioritizing bone health, cancer patients can support their overall recovery and quality of life.
Receiving a bone scan for cancer diagnosis can be an emotionally overwhelming experience. It's a pivotal moment that may induce feelings of fear, anxiety, and uncertainty about the future. Navigating these complex emotions is crucial for overall well-being and effective cancer management. Here, we offer guidance and resources to support your emotional and psychological journey following a diagnosis.
Seek Professional Help: It's pivotal to acknowledge when you need external support. A therapist or counselor specializing in cancer care can provide a safe space to express and work through your feelings. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) are evidence-based approaches that can help manage anxiety and depression related to cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Join Support Groups: Connecting with others who are going through similar experiences can provide a sense of community and understanding that is hard to find elsewhere. Many hospitals and cancer centers offer support groups facilitated by professionals. Online platforms and forums also offer accessible ways to find connection and support from the comfort of your home.
Focus on Nutrition: While not directly linked to emotional health, maintaining a balanced, vegetarian diet can play a role in overall well-being. Foods rich in antioxidants such as berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables can combat stress and anxiety by reducing oxidative stress in the body.
Explore Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help regulate emotions and alleviate stress. Setting aside time each day to engage in these practices can enhance your mood and provide a sense of peace during times of turmoil.
Utilize Community Resources: Look for community centers or non-profit organizations that offer resources and services for individuals facing cancer. These may include educational workshops, financial assistance programs, and recreational activities designed to support patients and their families.
Remember, it's vital to reach out and seek support rather than navigating this journey alone. Embracing community resources, nourishing your body with plant-based foods, and engaging in therapeutic practices can build resilience and provide the strength needed to face the challenges ahead.

Understanding the role of bone scans in the diagnosis and management of cancer can be complex. To simplify this vital area of oncology care, here's a compilation of frequently asked questions about bone scans for cancer patients, designed to demystify the process and alleviate concerns.
A bone scan is a nuclear imaging test that helps detect changes in the bones that may indicate cancer, infection, or other disorders. It's particularly necessary for cancer patients to identify metastasis, where cancer spreads to the bones from another part of the body, and to monitor the treatment's effectiveness.
Preparation for a bone scan is minimal. You might be asked to stay hydrated and possibly fast for a few hours before your appointment. It's also essential to inform your healthcare provider if you're pregnant or breastfeeding.
The procedure itself is not painful. You will receive a small amount of radioactive tracer through an injection. The sensation is similar to a regular shot. You might feel some discomfort from lying still during the scan.
The risks associated with bone scans are minimal. The amount of radiation exposure is low, comparable to that of a standard X-ray. Most patients do not experience any side effects, although a slight allergic reaction to the tracer is rare.
The entire process can take several hours. The tracer needs time to circulate and absorb into your bones, which can take 2-4 hours. The scanning part itself usually takes about 30-60 minutes.
After the bone scan, you can typically resume normal activities immediately. The tracer will naturally leave your body through urine, so staying hydrated post-scan is advisable to help flush it out faster.
A radiologist specializing in nuclear medicine will analyze your bone scan images and report the findings to your doctor. Areas that absorb more tracer might indicate cancer, but other conditions can cause similar patterns, so further testing may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Having straightforward, accessible information can make the journey through cancer diagnosis and treatment less daunting for patients and their families. We hope these FAQs have provided clarity on bone scans and their critical role in cancer care.