
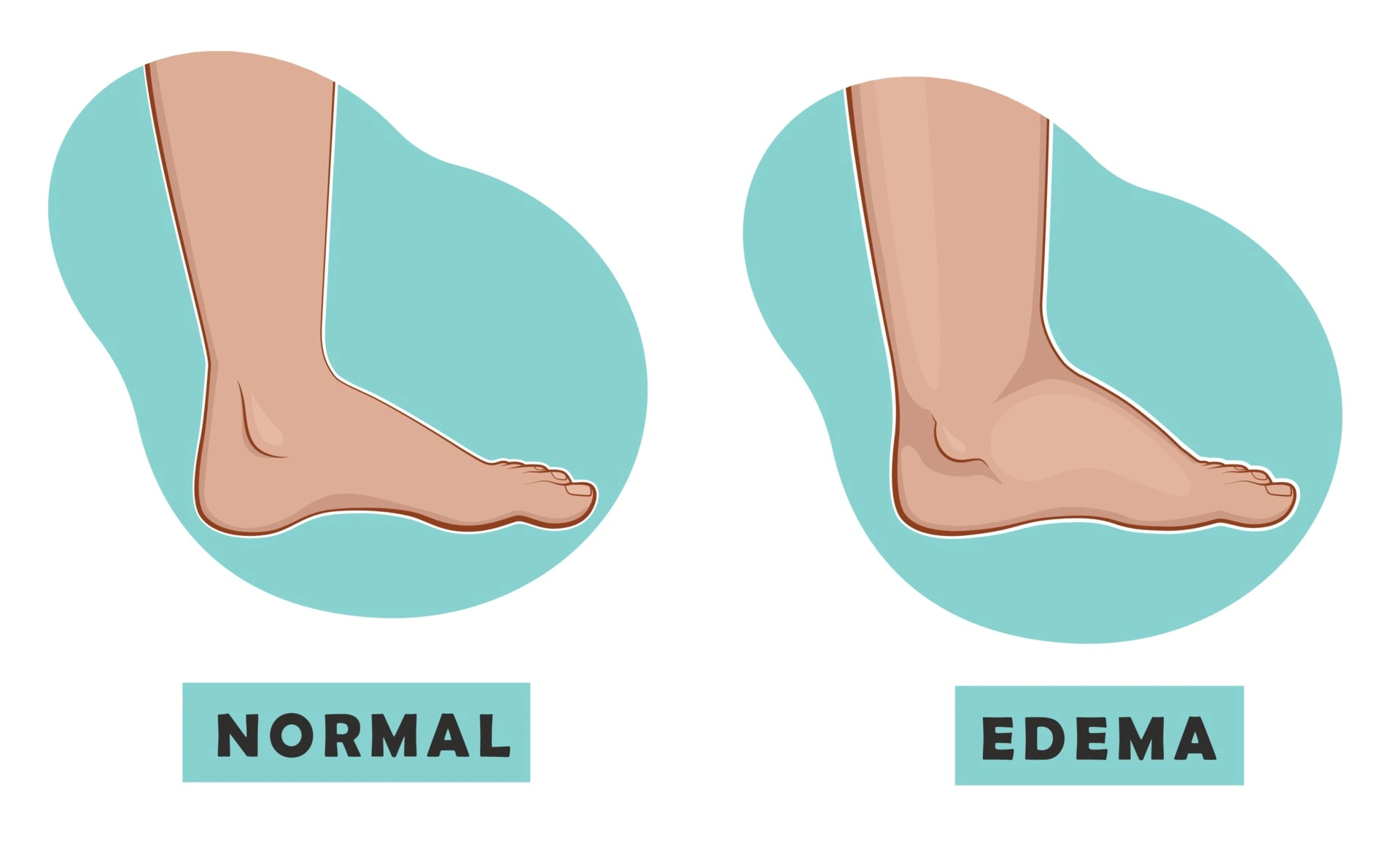
Edema, often known as swelling, is a common condition faced by cancer patients. It involves the accumulation of fluid under the skin or within body cavities. This condition can arise for various reasons in those battling cancer, making it critical to understand its underlying mechanisms, types, and common sites affected.
What is Edema?
At its core, edema is an accumulation of fluid in the body's tissues. While it can occur as a result of many conditions, in cancer patients, it's often linked directly to the cancer itself or as a side effect of treatments such as surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. Edema can lead to discomfort, pain, and sometimes more serious complications if not appropriately managed.
Why Edema Occurs in Cancer Patients
Several factors contribute to the development of edema in cancer patients. The tumor itself can press on vessels, restricting normal fluid flow. Some cancers can cause proteins in the blood to decrease, which affects the balance of fluids. Additionally, treatments like chemotherapy can damage cells, leading to inflammation and fluid accumulation.
Types of Edema in Cancer Patients
Common Sites for Edema
In cancer patients, common sites for edema include:
Managing edema effectively is crucial for cancer patients to reduce discomfort and prevent complications. Patients are advised to follow their healthcare provider's recommendations, which may include exercises, diet adjustments, and wearing compression garments. Including potassium-rich foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach in the diet can also help manage swelling.
Understanding edema in cancer patients is essential for managing and mitigating this condition. By recognizing the signs, knowing the types, and understanding the common sites affected, patients and caregivers can take proactive steps toward effective management and improved quality of life.
Swelling, or edema, in cancer patients, is a frequently encountered issue, which can be distressing and uncomfortable for the affected individuals. Understanding the various causes behind this swelling is crucial for managing and alleviating the symptoms. This section delves into the primary reasons why edema occurs in cancer patients, highlighting its correlation with different types of cancer treatments and the disease itself.
One significant cause of swelling in cancer patients is the surgical removal of lymph nodes. Lymph nodes often are removed or damaged during cancer treatment, especially in cases of breast, melanoma, and prostate cancers. This surgery can impede the natural flow of lymphatic fluid, leading to a condition known as lymphedema, where fluid accumulates in the limbs or other parts of the body.
Some chemotherapy drugs can induce swelling as a side effect. These medications can increase the retention of fluid, leading to edema, most commonly seen in the ankles, feet, and hands. Patients undergoing chemotherapy should be observant of any changes in their bodies and report excessive swelling to their healthcare provider.
In some instances, the cancer itself can be a direct cause of swelling. Tumors can block lymphatic vessels or veins, hindering the normal flow of lymph or blood, which results in fluid buildup. This is notably observable in cancers of advanced stages or where large tumors are present.
Besides medical causes, nutritional choices can also play a role in managing edema. Incorporating a balanced, plant-based diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help in reducing inflammation and supporting overall lymphatic function. Foods such as pineapple, which contains bromelain, and turmeric, known for its anti-inflammatory properties, can be beneficial additions to a cancer patient's diet.
Understanding the underlying causes of swelling in cancer patients is essential for effective management and treatment. By addressing these factors, patients can achieve better comfort and quality of life during their cancer journey. Patients and caregivers need to communicate openly with healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment and care plan that best suits the individual's needs.
Swelling, or edema, in cancer patients, can significantly impact the quality of life. It's often a side effect of cancer itself or a result of treatments such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation. Fortunately, there are practical steps both patients and caregivers can take to manage and treat edema effectively. Here, we'll explore a range of medical treatments and lifestyle changes that can help reduce swelling and improve comfort.
Starting with a professional consultation is crucial. Oncologists may recommend:
Beyond medical intervention, adjusting daily habits can play a significant role in managing edema. Consider the following:

To further minimize discomfort and improve the overall quality of life:
While managing edema in cancer patients can be challenging, leveraging medical treatments in conjunction with lifestyle modifications can markedly reduce swelling and enhance comfort. It's crucial to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor a plan that's best suited to individual needs and conditions. By taking a comprehensive approach, patients can significantly improve their quality of life.
Managing swelling, or edema, is a common challenge for cancer patients. It can cause discomfort, decrease mobility, and complicate treatment protocols. While medication and physical therapies are often prescribed, nutrition and diet play a crucial role in effectively managing edema in cancer patients. Understanding which foods may help reduce swelling and which could exacerbate it is essential for anyone undergoing cancer treatment.
Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help mitigate swelling. Below are some foods that have been recognized for their edema-fighting properties:
Just as some foods can help reduce swelling, others might exacerbate it. For cancer patients looking to manage edema, it is advisable to reduce or eliminate the following:
Drinking sufficient amounts of water is crucial for cancer patients experiencing swelling. Hydration can help flush toxins from the body and reduce water retention. Aim for 8-10 glasses of water daily, and consider incorporating hydrating fruits and vegetables, such as cucumbers and watermelon, into your diet.
Managing swelling through diet can be a potent tool for cancer patients. By emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods and limiting those that may exacerbate edema, patients can take an active role in their treatment and potentially enhance their quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially during cancer treatment.
Remember, every person's body reacts differently, and what works for one may not work for another. Tailoring your diet to your specific needs and reactions is crucial.
Swelling, or edema, can be a common and discomforting side effect for many cancer patients. Fortunately, specific exercises and physical therapy techniques can play a significant role in managing and reducing this swelling. These methods not only help in improving lymph flow but also contribute to enhancing the overall well-being of individuals undergoing cancer treatment.
Starting with gentle range-of-motion (ROM) exercises can significantly benefit cancer patients experiencing edema. These exercises involve moving a joint through its full range of movement to help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness. Simple activities such as slowly rotating the ankles and wrists, and stretching the arms can be effective. Always remember to perform these exercises within a comfortable range to prevent overexertion.
Walking is a low-impact exercise that can help stimulate lymphatic flow and reduce swelling. Initially, short walks, gradually increasing the duration as tolerated, can positively affect one's health. Walking improves cardiovascular health, enhances mood, and can be easily incorporated into the daily routine of cancer patients.
Elevating the legs above the level of the heart several times a day can greatly assist in reducing lower extremity swelling. Combining leg elevation with gentle yoga poses that promote circulation and lymph flow, like the "Legs-up-the-Wall" pose, can further alleviate swelling.
Manual Lymph Drainage Therapy is a specialized form of physical therapy. Trained therapists use light, rhythmic touches to encourage the natural drainage of the lymphatic system, helping to redirect fluid from swollen areas to more central areas of the body where the lymphatic system is functioning normally. It's important to seek a certified lymphedema therapist to perform MLD correctly and effectively.
Aquatic therapy in a warm, safe pool can be another excellent option for cancer patients dealing with edema. The buoyancy of water reduces stress on the body and joints, while the gentle resistance provided by water can help build strength and endurance. Furthermore, the hydrostatic pressure of water helps in reducing swelling and improving lymph flow.
Integrating exercises and physical therapy into the care plan of cancer patients can significantly help manage and reduce swelling. It is essential, however, to consult with healthcare providers before beginning any new exercise regimen, especially for those undergoing cancer treatment. Tailoring a program that fits an individual's needs and capabilities can lead to better management of edema and an improved quality of life.
Remember: Always listen to your body and adapt exercises as needed. The key is to start slowly, be consistent, and gradually increase intensity and duration as your body allows.
Edema, or swelling, is a common side effect faced by many undergoing cancer treatment. While clinical descriptions offer an understanding of the condition, personal stories can provide deeper insight and real-world coping strategies. Below, we share the experiences of individuals who have navigated the challenge of edema during their cancer journey, hoping to offer support and practical advice to others facing similar situations.
Anna's Story: Anna, diagnosed with breast cancer, experienced significant swelling in her arm, a condition known as lymphedema, post-surgery. Initially, it was frustrating; my arm felt heavy, and wearing my usual clothes became difficult, she recalls. Anna found relief through a combination of lymphatic drainage massage and wearing a compression sleeve. Incorporating gentle exercises and being mindful about not overstraining my arm was crucial, she adds. Anna also stresses the importance of finding a supportive community, Talking with others who understood what I was going through was incredibly comforting.
David's Experience: Kidney cancer survivor David faced edema in his legs. He notes that elevation, diet, and staying active within my limits were key. David learned that reducing sodium intake helped manage his swelling, along with ensuring he kept his legs elevated when resting. Joining a cancer support group introduced me to yoga and meditation, which not only helped with my swelling but also with my mental health, David shares.
Lisa's Approach: Dealing with ovarian cancer, Lisa encountered abdominal swelling. She found solace in dietary changes. Incorporating plants rich in anti-inflammatory properties like turmeric, ginger, and greens into my diet made a significant difference, Lisa recounts. Her advice is to listen to your body, Adjusting my diet according to how I felt each day was key in managing not just my edema, but also other side effects of treatment.
While each individual's experience with swelling during cancer treatment is unique, the overarching message from these stories is one of resilience and adaptability. Coping with edema is challenging, but with the right strategies and support, it is manageable. It's important to keep in close communication with your healthcare team and to not hesitate in seeking support from others. Remember, you're not alone in this journey.
For more information on coping with cancer and its side effects, follow our blog for regular updates and stories.
Dealing with swelling, medically known as edema, can be a distressing aspect of cancer and its treatment. Beyond the physical discomfort, swelling in cancer patients can have profound emotional and psychological ramifications. This is because changes in body image can significantly affect one's sense of self and overall mental health.
Swelling may lead to feelings of self-consciousness or a negative body image, as patients may struggle with visible changes in their appearance. This can complicate the already challenging experience of undergoing cancer treatment. Recognizing and addressing these psychological impacts is crucial for the holistic care of cancer patients.
The emotional toll of swelling in cancer patients can manifest in various ways, including:
Finding the right support system can make a significant difference in managing the emotional and psychological effects of swelling. Here are some resources that can help:
Patients and their families need to remember that they're not alone in this. Reaching out for help and accessing available resources can provide the necessary support to navigate the complex emotions and challenges presented by swelling in cancer.
For more information and support on dealing with swelling during cancer treatment, consider contacting cancer support organizations and healthcare providers specializing in oncology.
Swelling, or edema, can be a common symptom for cancer patients, arising due to the cancer itself or as a side effect of treatment. Being informed and asking your healthcare provider the right questions is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Here is a list of essential questions to discuss with your healthcare provider to better understand and cope with swelling during your cancer treatment:
Remember, open and honest communication with your healthcare provider is key to effectively managing your cancer treatment and any associated side effects like swelling. Don't hesitate to bring up any concerns or symptoms you are experiencing, no matter how minor they may seem.
Edema, or swelling, is a common side effect faced by cancer patients, often resulting from the cancer itself or as a result of treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery. While conventional medicine provides a foundation for managing edema, many patients are turning towards integrative and alternative therapies to find additional relief. Integrative therapies combine conventional and non-conventional methods to treat symptoms and improve quality of life. This section explores the efficacy of acupuncture, massage, and herbal supplements as supportive treatments for managing swelling in cancer patients.
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Research suggests that acupuncture might reduce chemotherapy-induced swelling by improving lymphatic flow. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology indicated that breast cancer patients who received acupuncture experienced significantly less post-operative swelling compared to those who did not. Patients interested in acupuncture should seek out a licensed practitioner with experience in cancer care.
Massage therapy can play a role in managing swelling by promoting lymph drainage and reducing fluid buildup. Specifically, manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), a gentle form of massage, is designed to enhance the circulation of lymph and can be particularly beneficial for patients with lymphedema. However, cancer patients need to consult with their healthcare team before starting massage therapy, as certain types of massage may not be appropriate depending on the cancer and treatment stages.
Some herbal supplements, like ginger and turmeric, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and may help manage swelling. Ginger, for instance, has been shown to reduce inflammation in various studies and can be included in the diet in many forms, such as teas or capsules. Turmeric, containing the active compound curcumin, may also reduce inflammation and swelling, but patients should approach herbal supplements with caution. Always consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplements to ensure they do not interact with cancer treatments.
In conclusion, integrating acupuncture, massage, and certain herbal supplements into a cancer patient's care plan can offer additional support for managing swelling, but it is crucial to do so under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Each patient's situation is unique, and treatments should be personalized to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Remember: Always discuss with your oncologist or healthcare team before starting any new therapy or supplement to ensure it complements your existing treatment plan safely.
Swelling, or edema, can be a common side effect for cancer patients, due to the cancer itself or as a result of treatment. While it can be manageable, edema can lead to serious complications such as infections, skin breakdown, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Below, find practical advice on how to prevent these serious health issues and understand when it's time to seek medical attention.
To prevent skin breakdown, it's crucial to keep the swollen area clean and moisturized. Use gentle, fragrance-free soaps and apply hypoallergenic lotions to keep the skin supple. Avoid tight clothing or accessories that could impair circulation or cause additional irritation. Regularly inspect your skin for any signs of redness, soreness, or infections and report these to your healthcare provider promptly.
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition where clots form in the deep veins, often in the legs. To reduce the risk, stay as active as your health permits. Gentle exercises, even simple leg movements while sitting, can improve circulation. Elevating your legs when possible and wearing compression stockings as prescribed can also help prevent DVT. Consult with your doctor before starting any new exercise regimen.
A balanced diet plays a key role in managing edema and preventing infections. Integrate foods rich in antioxidants and vitamins, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, into your daily meals. Foods high in potassium, like bananas and sweet potatoes, can also help manage swelling. Avoid excessive salt intake, as it can exacerbate fluid retention.
Ample hydration is essential to prevent complications from swelling. Drinking enough water helps to flush toxins from your body and supports overall health. Aim for at least 8 glasses a day, unless advised otherwise by your healthcare team.
If you notice increasing pain, swelling, redness, or warmth in the swollen area, these could be signs of infection or DVT and require immediate medical attention. Additionally, any new symptoms or sudden changes in your health should be discussed with your healthcare provider as soon as possible.
Managing edema requires a proactive approach to keep potential complications at bay. By adhering to these strategies, cancer patients can better safeguard their health and focus on their recovery. Remember, your healthcare team is your best resource for personalized advice and support.