
Hepatobiliary cancer refers to a group of cancers that affect the liver and bile ducts. These cancers are among the more complex and challenging to treat, given their critical location in the body's detoxification and digestion processes. Understanding the basics of hepatobiliary cancers is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Several types of cancers fall under the hepatobiliary category, including:

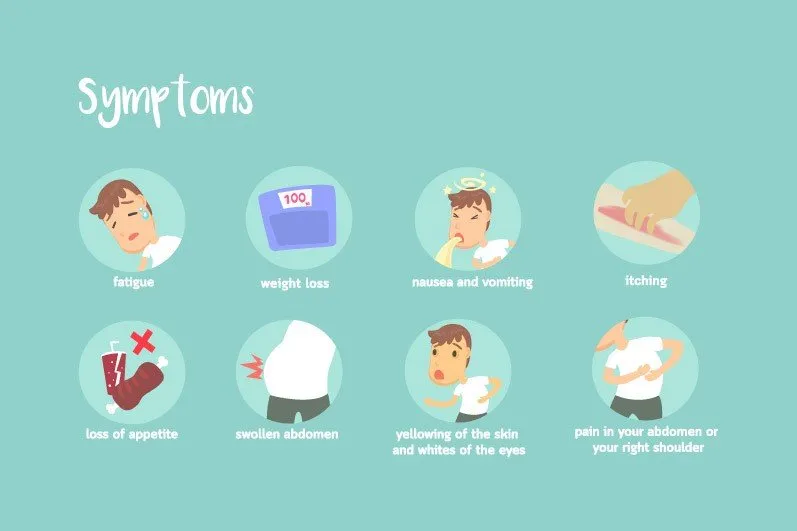
Symptoms of hepatobiliary cancer can be nonspecific but may include:
Diagnosis often involves a combination of blood tests, imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans, and sometimes a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
Treatment for hepatobiliary cancer may include:
While not all cases of hepatobiliary cancer can be prevented, understanding risk factors can help reduce your risk. These include:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help lower your risk of developing hepatobiliary cancer.
In summary, hepatobiliary cancer encompasses a variety of cancers affecting the liver and bile ducts. While it presents challenges in diagnosis and treatment, advances in medical research continue to improve outcomes for patients. Awareness of symptoms and risk factors is key to early detection and effective treatment.
Hepatobiliary cancer encompasses cancers of the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder. Understanding the terms associated with this group of cancers can help in grasping the disease's complexities. Here are some commonly used terms and their definitions.
Besides these terms, it's crucial to understand several diagnostic and treatment-related terms:
Understanding these terms can help patients and their families navigate the diagnosis and treatment of hepatobiliary cancers more effectively. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options.
Sure! Here is a simple, SEO-optimized content breakdown of the symptoms and signs of Hepatobiliary cancer in HTML format:
Hepatobiliary cancer includes cancers of the liver (hepatocellular carcinoma) and the bile ducts (cholangiocarcinoma). Recognizing the early symptoms of these cancers can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment. Below is a detailed list of common symptoms associated with Hepatobiliary cancer.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early detection of hepatobiliary cancer can greatly improve treatment outcomes.
Remember, having one or more of these symptoms does not necessarily mean you have hepatobiliary cancer, but its crucial to get them checked out by a healthcare provider.
This content structure utilizes SEO strategies by incorporating key phrases like "symptoms and signs of hepatobiliary cancer," "early symptoms of hepatobiliary cancer," and specific types of cancers within the hepatobiliary system. Moreover, it offers clear, concise, and valuable information aimed at improving understanding and awareness, thereby potentially increasing search engine ranking for these topics.
Hepatobiliary cancer, including cancers of the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder, requires careful diagnostic processes to ensure accurate detection and treatment planning. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here's how hepatobiliary cancer is generally diagnosed:
Following these diagnostic steps, doctors can determine the presence, type, and stage of hepatobiliary cancer, guiding treatment decisions. Remember, early detection through regular medical check-ups can increase the effectiveness of treatment. If you are at risk or experiencing symptoms associated with hepatobiliary cancer, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Hepatobiliary cancer, which affects the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder, is a complex disease requiring accurate diagnosis for effective treatment. Advanced diagnostic tests, including genetic testing, play a key role in identifying the specific nature and extent of the cancer. Below are some of the sophisticated tests used to diagnose hepatobiliary cancer:
Advanced imaging techniques are essential for diagnosing hepatobiliary cancer, helping to visualize the tumor and assess its impact.
A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope. It's the definitive way to diagnose hepatobiliary cancer. Techniques include:
Blood tests can check for markers that might indicate liver cancer, such as high levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP).
Genetic testing plays a pivotal role in the modern diagnosis and management of hepatobiliary cancer. It involves analyzing the DNA of cancer cells or the patient's genetic material to identify specific mutations that may drive the cancer:
Identifying genetic mutations helps in choosing targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective for individual patients, making personalized treatment possible for hepatobiliary cancer.
In conclusion, these advanced diagnostic tests and genetic analyses are crucial in the accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment of hepatobiliary cancer. They provide a detailed understanding of the tumor, facilitating tailored treatment approaches that can significantly improve outcomes for patients.
Hepatobiliary cancer refers to a group of cancers that affect the liver and bile ducts. Knowing the stages of this disease is crucial for treatment and prognosis. This article will walk you through the stages of hepatobiliary cancer, using clear and simple language.
At this earliest stage, abnormal cells are present but have not spread. It's also known as carcinoma in situ.
In Stage I, the cancer is present in the liver or bile ducts but has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant sites.
Stage II is divided into stages IIA and IIB, depending on the size and number of tumors and whether they have begun to spread to nearby blood vessels.
This stage is further categorized into IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC, which detail the cancer's spread to nearby organs, the portal vein, or arteries.
The most advanced stage of hepatobiliary cancer, Stage IV, indicates the cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes or organs.
Aside from the numerical stages, hepatobiliary cancers are also classified using the TNM system:
Knowing the stage of hepatobiliary cancer helps in determining the most effective treatment plan and prognosis. Regular check-ups and early diagnosis play a crucial role in managing the disease. If you or a loved one is dealing with hepatobiliary cancer, understanding these stages can empower you to make informed decisions about your health care.
Hepatobiliary cancer encompasses cancers of the liver and bile ducts. While it's not always possible to prevent these cancers completely, certain measures can reduce your risk. Follow these guidelines to help protect yourself.
Individuals at high risk for hepatobiliary cancers should undergo regular screening as per their doctor's advice. Early detection can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Limited exposure to carcinogens like aflatoxins (found in improperly stored grains) and avoiding tobacco smoke can further decrease the risk of hepatobiliary cancers.
Regular check-ups can help in early detection and management of conditions that could escalate to cancer, such as fatty liver disease or hepatitis infections.
Preventing hepatobiliary cancer involves a combination of lifestyle choices, vaccinations, and regular medical screenings. Taking active steps in these areas can significantly reduce your risk of developing these cancers.
Hepatobiliary cancers, affecting the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts, necessitate comprehensive treatment plans. The choice of treatment varies, depending on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Below are the primary treatment modalities utilized in combating hepatobiliary cancers.
The most definitive treatment for hepatobiliary cancer involves surgery, with the aim of removing the tumor completely. Options include:
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells, often administered through the vein (intravenously). It can be used:
Advances in understanding the molecular features of hepatobiliary cancers have led to the development of targeted therapy and immunotherapy. These treatments focus on specific aspects of cancer cells or the bodys immune response to fight the cancer. They often have different side effects than traditional chemotherapy, potentially offering a better quality of life during treatment.
In certain cases, radiotherapy is employed to destroy cancer cells using high-energy rays. It's particularly useful for controlling symptoms in advanced-stage diseases and in situations where surgery is not viable.
For a select group of patients, particularly those with early-stage liver cancer, a liver transplant might be considered an option. This involves replacing the liver with a healthy one from a donor.
In addition to treatments aimed at curing the cancer, palliative care is essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Offered alongside the curative treatments, it addresses the emotional, physical, and spiritual challenges posed by the disease.
Treating hepatobiliary cancer is a complex process that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Consultation with a team of specialists, including oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and palliative care experts, is critical to developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the patients specific situation.
Remember, the information provided here is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for diagnoses and treatment options suitable for your health condition.
Hepatobiliary cancer encompasses cancers of the liver and bile ducts. Treatment options include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Here's a concise overview of drugs commonly used in hepatobiliary cancer treatment.
These drugs represent the forefront of hepatobiliary cancer treatment, with ongoing research aimed at improving outcomes for patients. It's important to consult a healthcare professional for personalized treatment advice, as they can provide guidance based on an individual's specific condition and health status.
Hepatobiliary cancer encompasses malignancies that affect the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder. This type of cancer poses significant treatment challenges and requires a comprehensive approach. Integrative treatment strategies combine traditional methods with supportive therapies to address the disease from multiple fronts, aiming to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
The cornerstone of hepatobiliary cancer treatment often involves traditional methods such as:
Incorporating supportive therapies into the treatment plan focuses on the patient's overall well-being. These may include:
Every patient's journey with hepatobiliary cancer is unique, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment plans. Integrative treatment requires close collaboration among a multidisciplinary team including oncologists, surgeons, nutritionists, physical therapists, and mental health professionals. This team assesses the patient's specific needs, disease stage, and treatment responses to fine-tune the approach continuously.
Integrative treatment for hepatobiliary cancer aims to:
Embracing an integrative approach offers a holistic path to managing hepatobiliary cancer, focusing not just on the disease but on the person living with it. Those diagnosed with hepatobiliary cancer should discuss with their healthcare team the possibility of incorporating integrative treatment elements into their care plan.
Remember, the information provided here is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult with healthcare professionals before making decisions about medical care.
Hepatobiliary cancer, which includes liver cancer and bile duct cancer, is a complex condition that often requires integrated treatment approaches. Alongside conventional treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, many patients and healthcare providers explore the use of supplements to help manage symptoms, improve overall health, and possibly enhance treatment outcomes. However, it's critical to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplements, as they can interact with medications and affect liver function.
Vitamin D is frequently mentioned in the context of hepatobiliary cancer. Research suggests that vitamin D might have anticancer properties by promoting cancer cell death and reducing cell proliferation. Low levels of vitamin D are common in individuals with liver cancer, making supplementation potentially beneficial.
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health, which is often compromised in hepatobiliary cancer patients, especially those undergoing treatment. Probiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, potentially reducing the side effects of cancer treatments and supporting liver function.
Milk Thistle, known for its liver-protective qualities, is often used by patients with liver conditions, including hepatobiliary cancer. The active ingredient, silymarin, may help protect liver cells from damage and enhance liver function. However, its effectiveness and safety in cancer treatment require further research.
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, is recognized for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. In the context of hepatobiliary cancer, curcumin may help reduce inflammation and has been studied for its potential to inhibit cancer cell growth. However, its bioavailability is low, and it's often recommended to use it in conjunction with other substances that can increase its absorption, like piperine.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil and flaxseed, are praised for their anti-inflammatory effects. For hepatobiliary cancer patients, omega-3 supplements may help manage inflammation, potentially supporting liver health and improving the response to cancer treatments.
Choosing to integrate supplements into the management plan for hepatobiliary cancer should be a decision made with careful consideration and consultation with healthcare providers. Supplements can have a place in supporting health and treatment efficacy, but they are not a standalone treatment for cancer. Ensuring the safety and appropriateness of any supplement in the context of an individual's overall treatment plan is paramount.
Remember, the effectiveness and safety of supplements can vary, and what works for one person may not work for another. Continuous research and open discussions with healthcare professionals can help navigate the use of supplements in cancer care appropriately.
Living with hepatobiliary cancer presents unique challenges, including managing symptoms and treatment side effects. Engaging in certain activities can significantly improve quality of life for patients. Here are some recommended activities tailored for individuals with hepatobiliary cancer:
Remember, it's important to discuss any new activity with your healthcare provider to ensure it's safe for your specific condition. Balancing rest and activity is key to managing hepatobiliary cancer symptoms effectively.
Dealing with hepatobiliary cancer involves not just medical treatments but also incorporating self-care activities into your routine. These practices can significantly impact your well-being, helping manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here's a curated list of self-care strategies tailored for individuals fighting hepatobiliary cancer.
Focus on a nutrient-rich diet that supports liver health. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats into your meals. Consider consulting a dietitian specialized in cancer care for personalized dietary advice.
Stay on top of symptom management. This includes taking prescribed medications for pain, nausea, or other side effects as directed by your healthcare team. Don't hesitate to report new symptoms or changes in your condition.
Hydration is crucial. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily, but remember that your needs might vary, especially if experiencing vomiting or diarrhea. Consult your doctor for tailored advice.
Light to moderate exercise, as recommended by your healthcare provider, can boost energy levels and improve overall health. Activities such as walking, yoga, or light stretching can be beneficial. Always listen to your body and adjust activities as needed.
Ensure you're getting enough rest. Quality sleep helps the body repair and cope with the stresses of cancer treatment. Establish a regular sleeping schedule and create a restful environment.
Consider counseling or joining a support group for emotional and psychological support. Connecting with others who understand what you're going through can be incredibly comforting. Also, practices such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress.
Liver health can be further supported by avoiding things that can be harmful, such as alcohol, tobacco, and exposure to environmental toxins. Check with your doctor about what you should avoid.
Adopting these self-care activities alongside your medical treatments can make a significant difference in your journey with hepatobiliary cancer. Remember, every step taken towards self-care is a step towards a healthier you. Always consult with your healthcare team before making any changes to your diet, exercise, or treatment plan.
Dealing with Hepatobiliary cancer, which encompasses cancers of the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder, can be emotionally and physically taxing. Treatment for these cancers often involves surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these. Here are several strategies to help patients and their loved ones cope during this challenging time.
Remember, each patient's journey with Hepatobiliary cancer is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It's important to discuss any new coping strategies with your healthcare team to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your situation.
Keyword optimization: Hepatobiliary cancer, coping strategies, treatment, support groups, side effects, mental health.
While medical treatment is crucial for hepatobiliary cancer, incorporating certain home remedies can support overall health and potentially help with symptoms. Remember, always consult your healthcare provider before trying new home remedies.
While these home remedies may offer supportive benefits, they should not replace the treatments and interventions suggested by your healthcare team. It is essential to open a dialogue with your medical providers about any supplements or lifestyle changes you are considering.
Being informed about your hepatobiliary cancer and understanding the treatment options available are crucial steps in managing your condition. Below are essential questions that can help guide your discussions with your healthcare team, ensuring you are fully aware of your treatment journey.
Asking these questions allows you to play an active role in your hepatobiliary cancer treatment and care. Remember, your healthcare team is there to support you through this journey, so don't hesitate to reach out with any concerns or needs you might have.
Hepatobiliary cancers, which involve the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder, are among the most challenging cancers to treat. However, recent scientific breakthroughs have offered new hope, significantly improving treatment options and patient outcomes. This article outlines the latest advancements in the management of hepatobiliary cancer, showcasing innovative therapies and technologies.
Targeted therapy has emerged as a powerful approach for treating hepatobiliary cancers, focusing on specific genes, proteins, or the tumor environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival. Unlike chemotherapy, targeted therapies are designed to target cancer cells specifically, minimizing damage to normal cells. This advancement has led to the development of drugs that can block the growth and spread of cancer by interfering with specific molecules involved in the tumor growth and progression.
Immunotherapy represents a groundbreaking shift in cancer treatment, leveraging the body's immune system to fight the cancer cells. For hepatobiliary cancers, new immunotherapy treatments, including checkpoint inhibitors, have shown promising results. These drugs help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. In certain cases, immunotherapy has been used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy, to improve outcomes.
The precision of radiation therapy has significantly improved, thanks to technologies like stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and proton beam therapy. These advancements allow for high doses of radiation to be delivered to the cancer cells with minimal impact on the surrounding healthy tissue, increasing the effectiveness of treatment and reducing side effects.
Surgery remains a cornerstone in treating hepatobiliary cancer, especially for tumors that are caught early. The rise of minimally invasive surgical techniques, including laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery, has transformed the management of these cancers. These techniques offer several benefits, including smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
Genomic profiling is a personalized medicine approach that analyzes the patient's tumor to identify specific genetic mutations responsible for cancer growth. This information can then guide the choice of targeted therapies that are most likely to be effective for the individual patient, contributing to more personalized and effective treatment plans.
The landscape of hepatobiliary cancer treatment is rapidly evolving, with new therapies and technologies offering improved outcomes and quality of life for patients. Continued research and clinical trials are essential to further advance these treatments and uncover new opportunities for managing this challenging group of cancers.
After completing treatment for hepatobiliary cancer, which includes cancers of the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts, patients will need to undergo follow-up care to monitor recovery and watch for any signs of cancer recurrence. This care is crucial for managing side effects, detecting any new cancers, and supporting the patient's overall well-being. Here's what you need to know about the follow-up care necessary after hepatobiliary cancer treatment.
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are essential after hepatobiliary cancer treatment. These visits typically include physical exams, blood tests to check liver function and to look for tumor markers, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans. The frequency of these appointments will depend on the original cancer's stage and location, the type of treatment received, and the individual patient's health condition.
Making healthy lifestyle adjustments can aid in recovery and improve your quality of life after cancer treatment. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, staying physically active, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress. Your healthcare team can provide personalized recommendations based on your unique needs.
Treatment for hepatobiliary cancers often comes with side effects, which can vary depending on the type of treatment received. Common side effects include fatigue, digestive issues, and changes in weight. It's important to report any side effects to your healthcare provider, as there are many strategies and medications that can help manage them effectively.
Dealing with cancer and its treatment can be mentally and emotionally challenging. It's essential to seek psychological support if needed. Support groups, counseling, and therapy can provide valuable spaces for expressing feelings, coping with stress, and connecting with others who have had similar experiences.
One of the primary goals of follow-up care is to monitor for any signs of cancer recurrence. It's crucial to attend all scheduled appointments and to report any new symptoms or changes in health to your healthcare provider immediately. Early detection of a recurrence can often lead to more effective treatment.
Follow-up care after hepatobiliary cancer treatment is a critical component of a patient's recovery and long-term health. It involves regular check-ups and monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, managing side effects, psychological support, and vigilance for any signs of cancer recurrence. By attending all follow-up appointments and maintaining open communication with the healthcare team, patients can enhance their quality of life and increase their chances of a successful recovery.
Being in remission from hepatobiliary cancer marks a significant milestone. However, maintaining your health and minimizing the risk of recurrence remains crucial. Below are essential considerations to help you stay healthy during remission.
Adhering to a schedule of regular check-ups is paramount. These appointments allow your healthcare team to monitor your health, detect any signs of cancer returning early, and manage long-term side effects of previous treatments. Ensure to keep all your appointments and discuss any health concerns with your doctors.
Eating a balanced diet is critical for keeping your body strong and reducing the risk of cancer recurrence. Focus on incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals. Consider consulting a dietitian who can tailor a nutritional plan suited to your specific needs post-cancer treatment.
Exercise plays a vital role in improving your overall health and well-being during remission. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, alongside strength training exercises at least two days a week. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
Alcohol and tobacco are known risk factors for hepatobiliary and other types of cancers. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking can significantly reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and support your overall health recovery.
The emotional impact of cancer and its treatment can be profound. Engaging in stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling can help improve your emotional well-being. Joining a support group can also provide comfort and understanding from others who have experienced similar journeys.
Being vigilant about any new or unusual symptoms is crucial. Early detection of recurrence can significantly impact the effectiveness of treatment. Communicate openly with your healthcare team about any concerns, no matter how small they may seem.
By focusing on these key areas, individuals in hepatobiliary cancer remission can take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and well-being. Remember, your healthcare team is your best resource for advice and support tailored to your unique situation.
Hepatobiliary cancer refers to malignancies that occur in the liver (hepatocellular carcinoma), gallbladder, and bile ducts (cholangiocarcinoma). These types of cancer are significant due to their complexity and the vital roles of the organs involved. Below are some commonly asked questions related to Hepatobiliary Cancer.
Symptoms can vary depending on the specific type of cancer and its stage but may include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, nausea, and changes in stool or urine color. Early stages often have no symptoms.
Diagnosis can involve a combination of blood tests, imaging tests (such as CT scans, MRI, or ultrasounds), and biopsies to confirm the presence of cancer and assess its stage.
Treatment varies greatly depending on the type and stage of the cancer but may include surgery to remove tumors, liver transplantation, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
While not all cases are preventable, you can reduce your risk by limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, managing hepatitis infections properly, and avoiding exposure to toxins that can damage the liver.
The prognosis can vary significantly based on the type and stage of cancer at diagnosis, the patient's overall health, and the response to treatment. Early detection and timely treatment greatly improve outcomes.
Yes, there are several support groups and organizations dedicated to providing information, support, and advocacy for individuals with Hepatobiliary Cancer and their families. It can be beneficial to connect with others who understand the journey.
These FAQs provide a starting point for understanding Hepatobiliary Cancer. If you or a loved one have been diagnosed, it's important to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized information and treatment options.